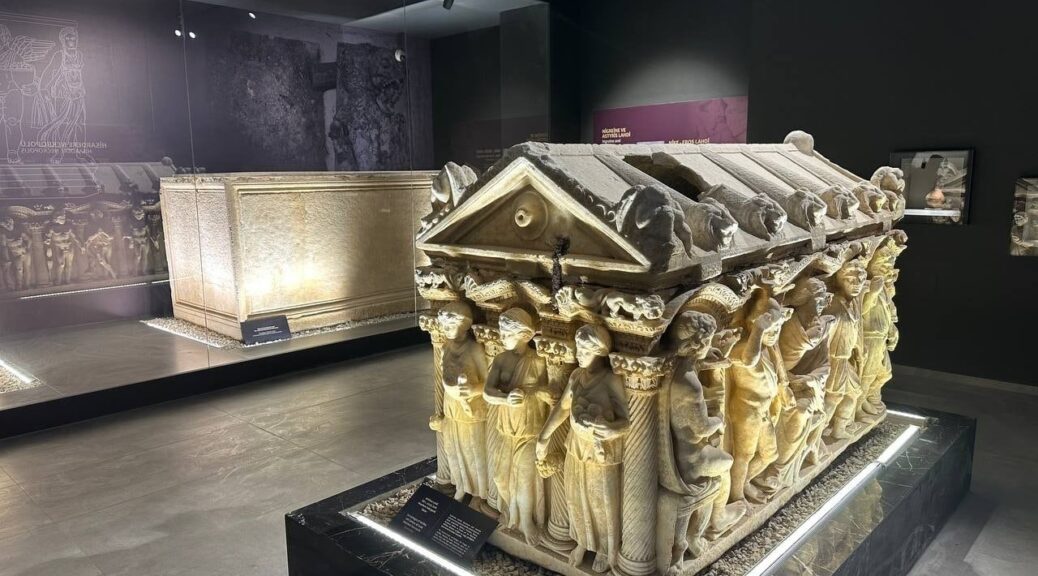
The Secret of the Shipwrecks at Theodosius Harbor: 1,600 Years Old Women’s Sandals and Comb

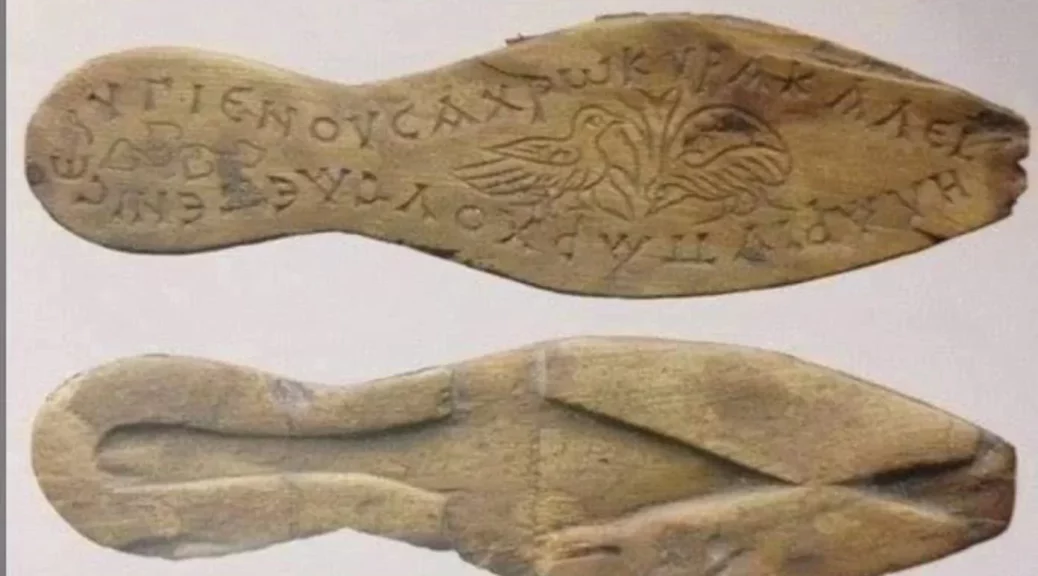
The 1,600-year-old sandals and comb unearthed during the excavations of Theodosius Harbor (Portus Theodosiacus), the second-biggest harbor built on the coast of the Marmara Sea, fascinate those who see it.
Excavations conducted concurrently with the construction of the Marmaray and Metro rail projects initiated to provide a solution to Istanbul’s transportation problems have resulted in the most extensive archeological survey in the city’s history.
As a result, detailed information about Istanbul’s prehistoric periods has been obtained, an area that has hosted different cultures for thousands of years and unites the cultures of the East and the West.
Before 2004, information about the settlement history of Istanbul was based on excavations outside the Historic Peninsula; settlements in these areas could be traced to 2,500 years ago.
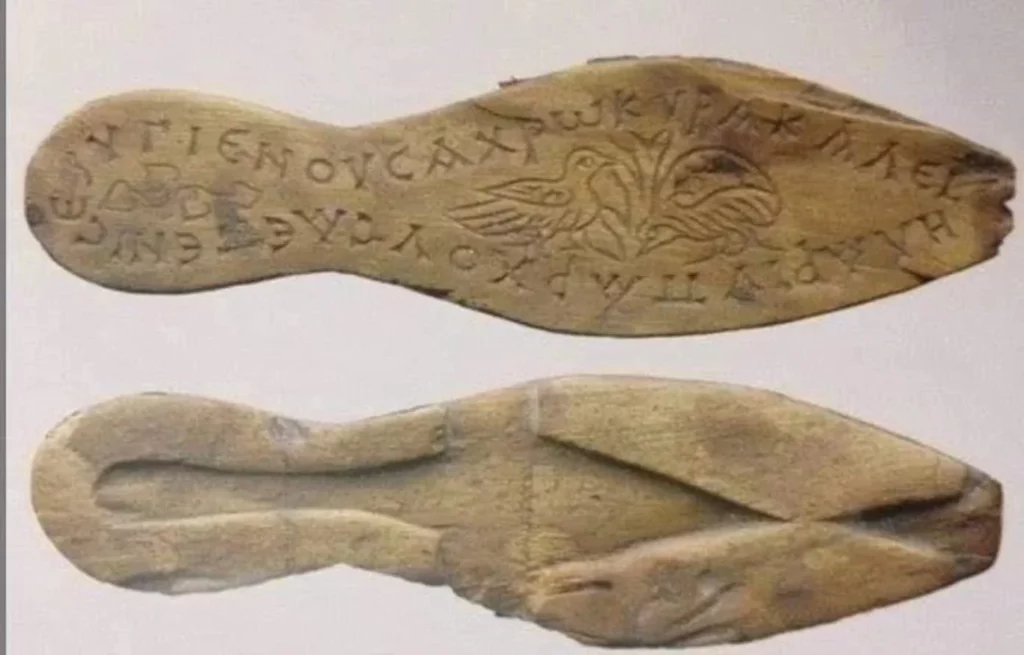

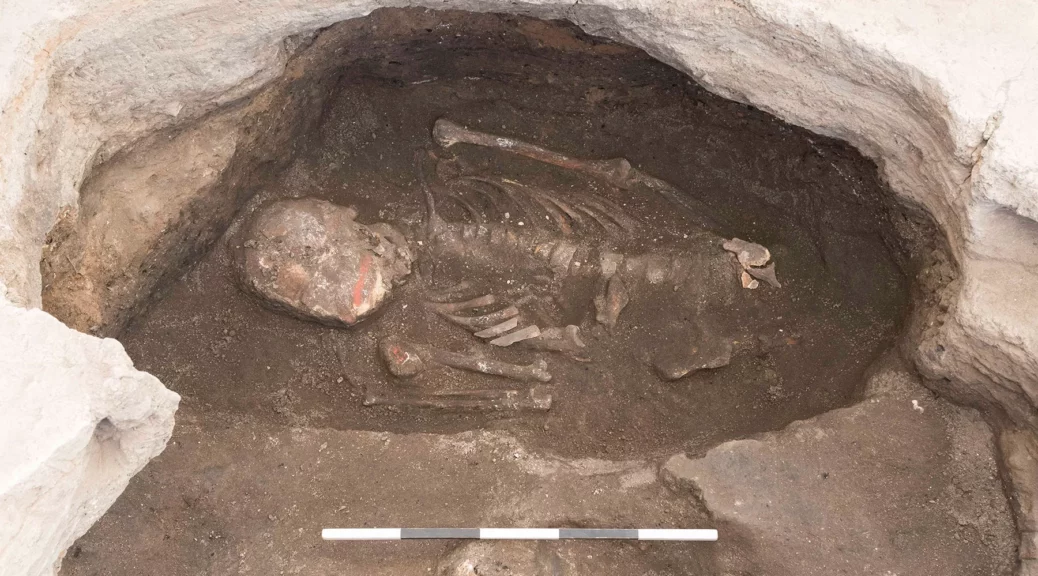
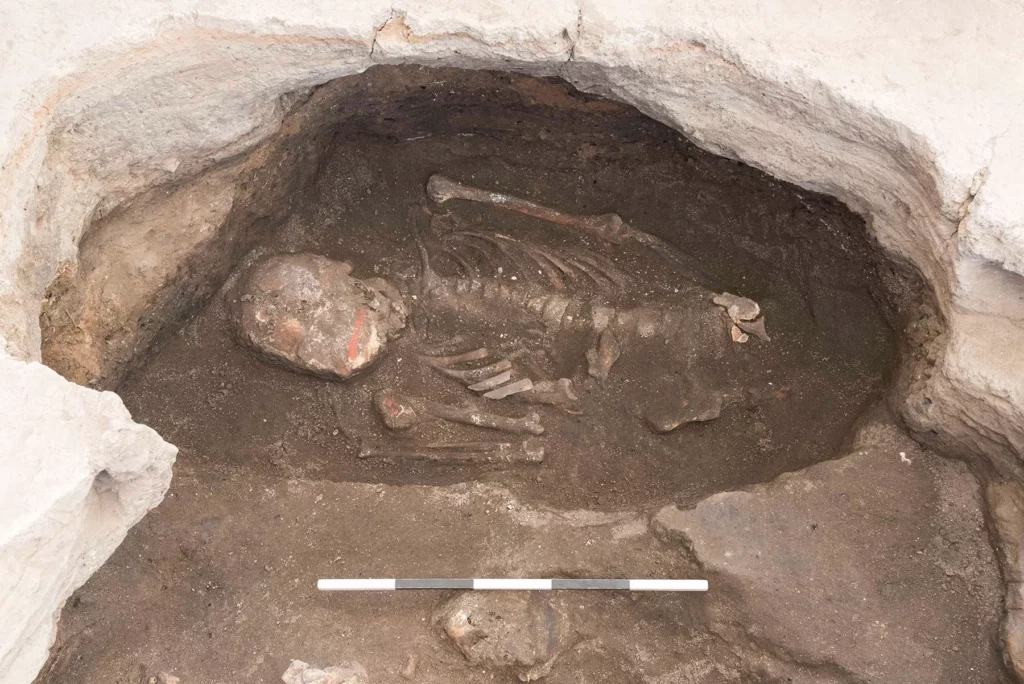
The astonishing finds were discovered during digs prompted by the Marmaray project. One of these interesting finds was sandals with wooden soles belonging to a woman.
The sandals had a Greek message that reads: “Use in health, lady, wear in beauty and happiness.”
Researchers came to differing conclusions about the sunken ships discovered in the harbor of Theodosius, which dated from different centuries. It was suggested that the ships might have sunk during a hurricane, tsunami, or other natural disaster.
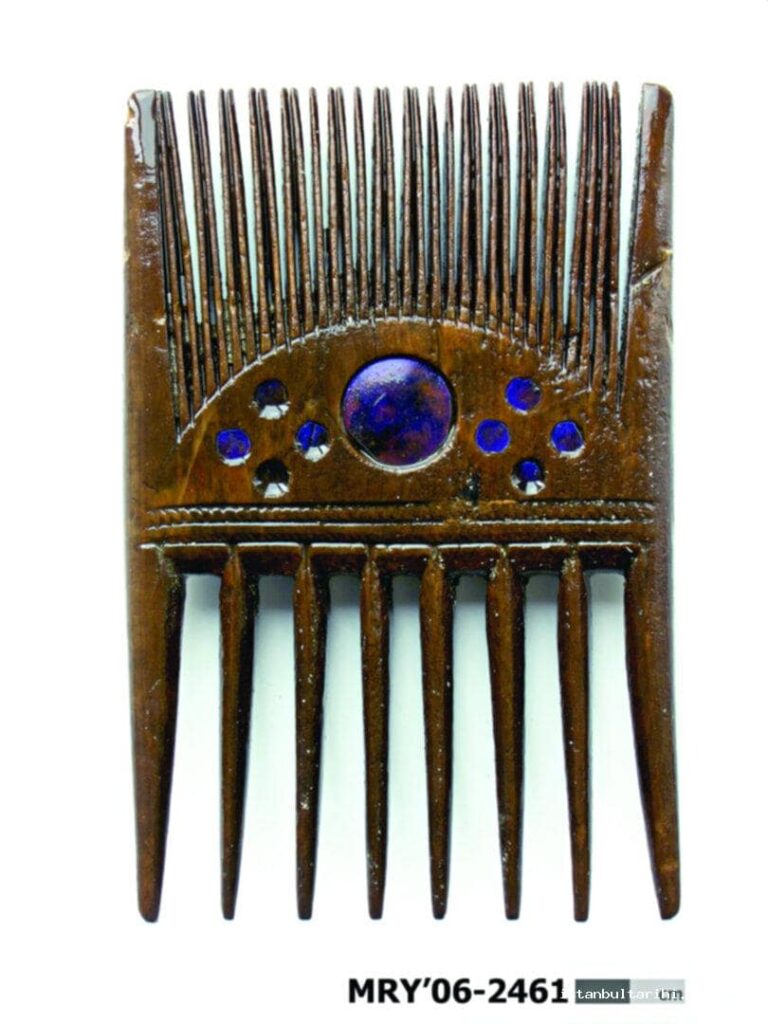

The idea that the ships were simply abandoned after serving their purpose is one of the most widely held theories. In the fourth of nine stratigraphic segments in the excavation field, researchers discovered evidence of the effects of the earthquake and tsunami that occurred in AD 553.
Another theory is that the southwesterly wind, known as kaçak (fugitive) in Turkish, which begins suddenly in the Marmara Sea during the summer months, caused these vessels to sink.
Above the vessels, a thick layer of sea sand formed. The accumulation that filled the harbor protected and preserved the sunken ships.
The rapid burial of the ships created an anoxic environment that preserved rigging tools like tackles, pulleys, ropes, and toggles as well as everyday items like combs, leather sandals, straw baskets, and wooden plates as well as a variety of organic and inorganic artifacts like stone and iron anchors.
Around the harbor, a number of fragments of sunken ships and items from earlier eras were also discovered.